“
However, sometimes parents notice that speech is not easy for a child: letters sound wrong, words are incomprehensible, sentences are not coordinated. Then the child should be brought to a consultation with a specialist – a speech therapist.
The individual characteristics of some children are exacerbated by the full-scale war with Russia in Ukrainian realities. Speech therapists note that the lack of basic safety in children affects the development of speech skills – there are more cases of dysarthria (speech disorder) or logoneurosis (stuttering), dyslalia (pronunciation disorder), dyslexia (reading disorder) and dysgraphia (writing disorder).
Currently, not every kindergarten or school has a speech therapist on staff, so parents should understand what to pay attention to in order to start corrective classes on time.
“Ukrainian Pravda. Life” asked speech therapists who cooperate with the project “Preparing children and youth for the future” of the international charity fund Caritas of Ukraine in different regions of the country to share their experience. Specialists described situations and “bells” that cannot be ignored when a child learns to speak, read and write.
Delay in vocabulary development Babies make their first attempts to communicate with the world before they are a year old. In the period of 9-12 months, babies show babbling and babbling: the sounds “gii”, “agu”, “khh”, “bobo”, “tutu” etc. are typical for early age. If they are absent, then this is a reason to consult a neurologist.
“The most favorable period for language development is the age of 2-3 years, when the child should actively replenish the vocabulary and compose phrases“, the speech therapist notes Oksana Zatorska from Caritas Drohobych. According to her, if at this age the child “understands everything, but is silent”, or his vocabulary does not exceed 10-12 words, then it is worth consulting.
It is important to understand that the idioms “haw”, “meow”, “bb” and others are not words. “Own language”, which is unclear and unintelligible to the environment, does not count either. Words should contain semantics and be commonly used: “mom”, “dad”, “cat”, “grandma”, “give”, “want”, “drink”, etc.
“If at this age the child constantly repeats other people’s words and phrases in his speech, in particular from cartoons and movies, it is worth contacting a speech therapist. Words or phrases can also be in a foreign language“, he clarifies speech therapist Ruslana Kurii from Caritas Boryslav.
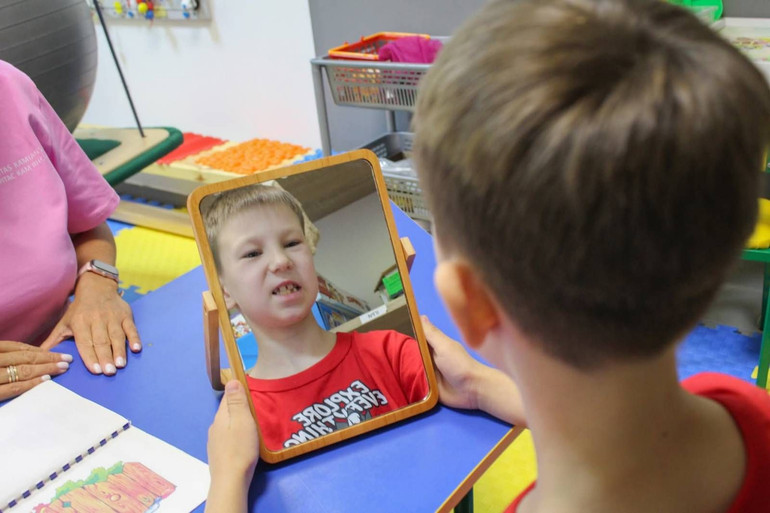 The child works with a speech therapist
The child works with a speech therapist
Photo: Caritas of Ukraine
Physiological features of the development of the articulatory apparatus Correct pronunciation depends on the structure and coordinated work of such organs as the tongue, lips, jaws, palate and uvula, alveoli, vocal cords and back wall of the pharynx.
Each of them is responsible for its function: the tongue ensures the accuracy of reproduction of sounds and syllables, the lips form lip sounds, the jaws affect the strength and clarity of articulation, the palate and tongue regulate timbre and resonance.
Also important are the bite, the development of the lower jaw, the length of the lingual frenulum, and the presence or absence of a “Gothic” palate. All of these factors determine how well a child can correctly reproduce sounds, words, and whole phrases.
“Sometimes parents notice that the child does not speak, and his mouth is constantly open. At the same time, the tongue lies between the teeth or is pushed forward. The child still has problems chewing solid food, and the pronunciation of most sounds is unclear. These are screenings before checking the development of the articulatory apparatus“, he explains speech therapist Lilia Titova from Caritas Kolomyia.
Attention should also be paid to the health of the nasopharynx and hearing.
“If a child has frequent diseases of the nasopharynx and the development of adenoid tissues from an early age, this can cause partial blockage of the airways and ear canals. As a result, the child is forced to breathe through his mouth and speaks less. She may also be deaf in one ear and have persistent otitis media“, specialists list.
Physiological disorders directly affect the quality of speech and the development of phonemic hearing, on which further successful literacy training depends. That is why a timely consultation with an ENT doctor and a speech therapist will help to identify and correct problems, preventing the establishment of incorrect speech habits.
Bad pronunciation of sounds Funny twisting of words by a child at the age of 4-5 often becomes a family legend, such words are written down and remembered. Grandparents are happy, and parents think that it will “outgrow” with time. However, for many, problems with sound pronunciation do not go away on their own.
“If the child replaces one sound with another, omits or distorts them, this is the first sign that the help of a speech therapist is needed. “Elephant – dream”, “hands – bows”, “spoon – ladle”, “kettle – kettle“, – gives examples speech therapist Halyna Rybchuk from Caritas Brody.
“Substitution of letters that are similar in sound (b – p, d – t, z – s, w – z), rearrangement of syllables or omission of letters may indicate underdevelopment of phonemic hearing, which in the future may cause difficulties in mastering writing“, he adds speech therapist Yulia Leshchenko from Caritas Kamianske.
In complex cases, when the child does not distinguish sounds and letters in words by ear, this may be a dyslalia disorder pronunciation of sounds.
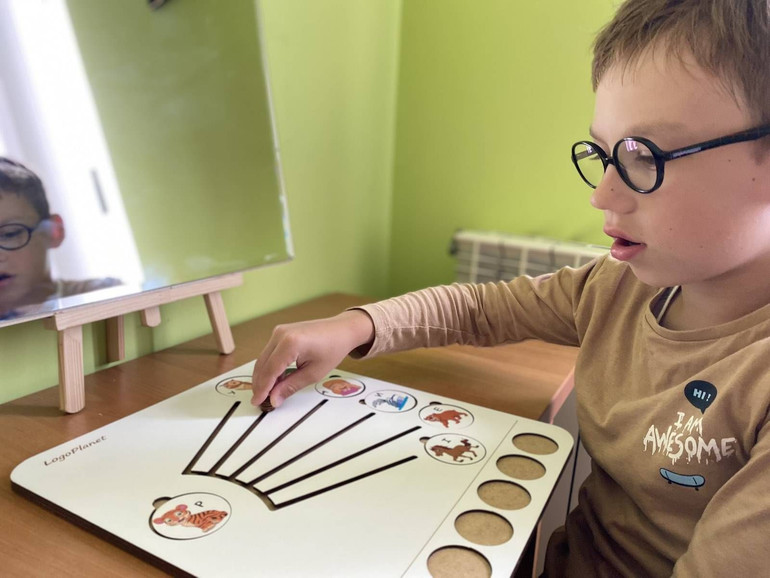 The child works with a speech therapist
The child works with a speech therapist
Photo: Caritas of Ukraine
Speech perception difficulties It happens that the child “hears, but does not understand“. For example, a teacher in a kindergarten asks: “Take a red pencil and draw the sun at the top of the sheet”, and the child draws in blue or does not complete the task at all. The problem may not be in attention, but in speech perception and information processing.
“It is very important that the child develops a good perception of information by ear, so that in the future it does not complicate learning, because most of the instructions at school are given verbally“, he emphasizes speech therapist Tetyana Razumova from Caritas of Odessa.
If a child grows up in a Russian-speaking environment, it negatively affects his understanding and phonetic distinction of Ukrainian-language educational content at school.
Jokes about the “Russian-speaking jaw” are not really jokes if we are talking about children. Speech therapists do not directly retrain the understanding of another language, but they can help a child cope with the difficulties of learning new sounds and accents.
Incorrect sentence formation When a child makes systematic mistakes in the construction of sentences – puts words together incorrectly, confuses genders or cases (“Mom went to the store”, “The bunny eats a carrot”) – it is not just children’s jokes, but a symptom of speech difficulties. It is important for speech therapists to work with such children even before school.
“It happens that a child at the age of 5-6 can pronounce single words and simple sentences without problems, but when asked to tell about his day, retell a cartoon or make a story based on a picture, he gets lost. Her story is illogical, consists of fragments, words can be rearranged, and important details are omitted“, Liliya Titova describes the possible situation.
Slow or too fast pace of speech Some children speak intermittently, as if they get “stuck” on words and repeat syllables (“ma-ma-ma machine”). Their speech is very slow, with long pauses.
“They seem to pick up every word and this causes difficulties in communication“, says Ruslana Kurii.
And there are children who, on the contrary, “scribble” too quickly, swallowing the endings of words and skipping syllables. Few people understand them. Over time, this affects the psychological state of the child, he begins to feel shy and avoid communication.
Both cases can indicate dysarthria or logoneurosis (stuttering), notes Yulia Leshchenko.
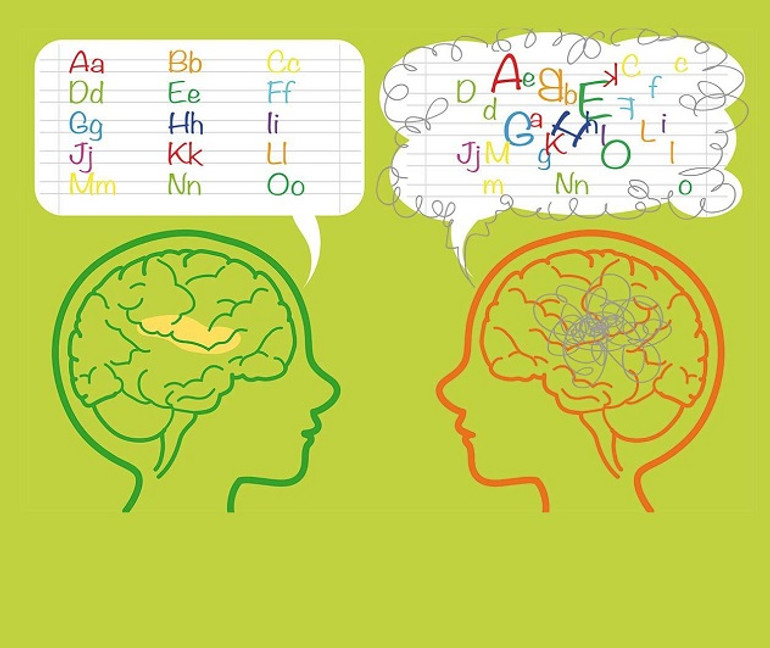
Problems with writing and reading In children 6-7 years old, at the initial stage of learning to read and write, omissions of letters, syllables or distortion of words can happen quite often. This is related to the formation of skills and attention.
If, after several months of training and the teacher’s explanations, the student still writes: “sapka” instead of “cap”, “tim” instead of “home” in dictation. Or omits/adds letters (cat – ki, milk – molo), rearranges syllables (table – salt), writes “joined” words (ushkolupishov), then this is a signal that the child has difficulties with the formation of written speech.
“Orally, the child can formulate sentences correctly, but when writing and reading, he constantly skips letters, replaces letters that are similar in sound or spelling (l – m, i – sh, d – t), then this is dyslexia or dysgraphia. It is necessary to work with this additionally“, Halyna Rybchuk concludes.
Olga Sytnikespecially for UP. Life

”, — write: www.pravda.com.ua
However, sometimes parents notice that speech is not easy for a child: letters sound wrong, words are incomprehensible, sentences are not coordinated. Then the child should be brought to a consultation with a specialist – a speech therapist.
The individual characteristics of some children are exacerbated by the full-scale war with Russia in Ukrainian realities. Speech therapists note that the lack of basic safety in children affects the development of speech skills – there are more cases of dysarthria (speech disorder) or logoneurosis (stuttering), dyslalia (pronunciation disorder), dyslexia (reading disorder) and dysgraphia (writing disorder).
Currently, not every kindergarten or school has a speech therapist on staff, so parents should understand what to pay attention to in order to start corrective classes on time.
“Ukrainian Pravda. Life” asked speech therapists who cooperate with the project “Preparing children and youth for the future” of the international charity fund Caritas of Ukraine in different regions of the country to share their experience. Specialists described situations and “bells” that cannot be ignored when a child learns to speak, read and write.
Delay in vocabulary development Babies make their first attempts to communicate with the world before they are a year old. In the period of 9-12 months, babies show babbling and babbling: the sounds “gii”, “agu”, “khh”, “bobo”, “tutu” etc. are typical for early age. If they are absent, then this is a reason to consult a neurologist.
“The most favorable period for language development is the age of 2-3 years, when the child should actively replenish the vocabulary and compose phrases“, the speech therapist notes Oksana Zatorska from Caritas Drohobych. According to her, if at this age the child “understands everything, but is silent”, or his vocabulary does not exceed 10-12 words, then it is worth consulting.
It is important to understand that the idioms “haw”, “meow”, “bb” and others are not words. “Own language”, which is unclear and unintelligible to the environment, does not count either. Words should contain semantics and be commonly used: “mom”, “dad”, “cat”, “grandma”, “give”, “want”, “drink”, etc.
“If at this age the child constantly repeats other people’s words and phrases in his speech, in particular from cartoons and movies, it is worth contacting a speech therapist. Words or phrases can also be in a foreign language“, he clarifies speech therapist Ruslana Kurii from Caritas Boryslav.
 The child works with a speech therapist
The child works with a speech therapist
Photo: Caritas of Ukraine
Physiological features of the development of the articulatory apparatus Correct pronunciation depends on the structure and coordinated work of such organs as the tongue, lips, jaws, palate and uvula, alveoli, vocal cords and back wall of the pharynx.
Each of them is responsible for its function: the tongue ensures the accuracy of reproduction of sounds and syllables, the lips form lip sounds, the jaws affect the strength and clarity of articulation, the palate and tongue regulate timbre and resonance.
Also important are the bite, the development of the lower jaw, the length of the lingual frenulum, and the presence or absence of a “Gothic” palate. All of these factors determine how well a child can correctly reproduce sounds, words, and whole phrases.
“Sometimes parents notice that the child does not speak, and his mouth is constantly open. At the same time, the tongue lies between the teeth or is pushed forward. The child still has problems chewing solid food, and the pronunciation of most sounds is unclear. These are screenings before checking the development of the articulatory apparatus“, he explains speech therapist Lilia Titova from Caritas Kolomyia.
Attention should also be paid to the health of the nasopharynx and hearing.
“If a child has frequent diseases of the nasopharynx and the development of adenoid tissues from an early age, this can cause partial blockage of the airways and ear canals. As a result, the child is forced to breathe through his mouth and speaks less. She may also be deaf in one ear and have persistent otitis media“, specialists list.
Physiological disorders directly affect the quality of speech and the development of phonemic hearing, on which further successful literacy training depends. That is why a timely consultation with an ENT doctor and a speech therapist will help to identify and correct problems, preventing the establishment of incorrect speech habits.
Bad pronunciation of sounds Funny twisting of words by a child at the age of 4-5 often becomes a family legend, such words are written down and remembered. Grandparents are happy, and parents think that it will “outgrow” with time. However, for many, problems with sound pronunciation do not go away on their own.
“If the child replaces one sound with another, omits or distorts them, this is the first sign that the help of a speech therapist is needed. “Elephant – dream”, “hands – bows”, “spoon – ladle”, “kettle – kettle“, – leads and examples speech therapist Halyna Rybchuk from Caritas Brody.
“Substitution of letters that are similar in sound (b – p, d – t, z – s, w – z), rearrangement of syllables or omission of letters may indicate underdevelopment of phonemic hearing, which in the future may cause difficulties in mastering writing“, he adds speech therapist Yulia Leshchenko from Caritas Kamianske.
In complex cases, when the child does not distinguish sounds and letters in words by ear, this may be a dyslalia disorder pronunciation of sounds.
 The child works with a speech therapist
The child works with a speech therapist
Photo: Caritas of Ukraine
Speech perception difficulties It happens that the child “hears, but does not understand“. For example, a teacher in a kindergarten asks: “Take a red pencil and draw the sun at the top of the sheet”, and the child draws in blue or does not complete the task at all. The problem may not be in attention, but in speech perception and information processing.
“It is very important that the child develops a good perception of information by ear, so that in the future it does not complicate learning, because most of the instructions at school are given verbally“, he emphasizes speech therapist Tetyana Razumova from Caritas of Odessa.
If a child grows up in a Russian-speaking environment, it negatively affects his understanding and phonetic distinction of Ukrainian-language educational content at school.
Jokes about the “Russian-speaking jaw” are not really jokes if we are talking about children. Speech therapists do not directly retrain the understanding of another language, but they can help a child cope with the difficulties of learning new sounds and accents.
Incorrect sentence formation When a child makes systematic mistakes in the construction of sentences – puts words together incorrectly, confuses genders or cases (“Mom went to the store”, “Bunny eats carrots”) – this is not just children’s jokes, but a symptom of speech difficulties. It is important for speech therapists to work with such children even before school.
“It happens that a child at the age of 5-6 can pronounce single words and simple sentences without problems, but when asked to tell about his day, retell a cartoon or make a story based on a picture, he gets lost. Her story is illogical, consists of fragments, words can be rearranged, and important details are omitted“, Liliya Titova describes the possible situation.

Slow or too fast pace of speech Some children speak intermittently, as if they get “stuck” on words and repeat syllables (“ma-ma-ma machine”). Their speech is very slow, with long pauses.
“They seem to pick up every word and this causes difficulties in communication“, says Ruslana Kurii.
And there are children who, on the contrary, “scribble” too quickly, swallowing the endings of words and skipping syllables. Few people understand them. Over time, this affects the psychological state of the child, he begins to feel shy and avoid communication.
Both cases can indicate dysarthria or logoneurosis (stuttering), notes Yulia Leshchenko.
Problems with writing and reading In children 6-7 years old, at the initial stage of learning to read and write, omissions of letters, syllables or distortion of words can happen quite often. This is related to the formation of skills and attention.
If, after several months of training and the teacher’s explanations, the student still writes: “sapka” instead of “cap”, “tim” instead of “home” in dictation. Or omits/adds letters (cat – ki, milk – molo), rearranges syllables (table – salt), writes “joined” words (ushkolupishov), then this is a signal that the child has difficulties with the formation of written speech.
“Orally, the child can formulate sentences correctly, but when writing and reading, he constantly skips letters, replaces letters that are similar in sound or spelling (l – m, i – sh, d – t), then this is dyslexia or dysgraphia. It is necessary to work with this additionally“, Halyna Rybchuk concludes.
Olga Sytnikespecially for UP. Life

