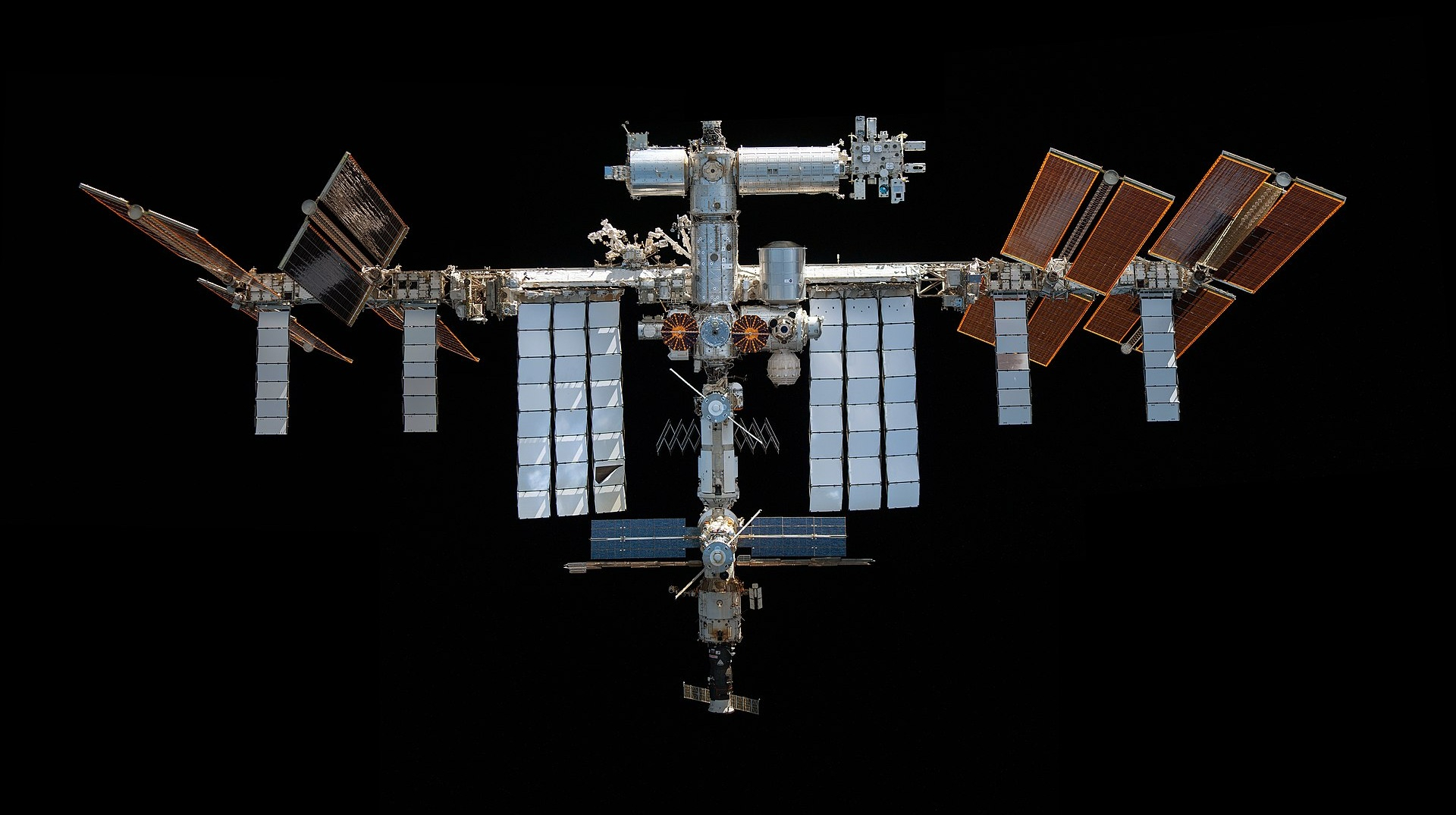
“Construction of the first module of the International Space Station “King”, based on the project of a functional-load module for the Soviet station “Mir”, began more than 30 years ago, in 1994.”, – WRITE: mezha.media
The next module, “Zvezda”, was launched only on July 12, 2000 and wasately stimulated with two other July 26, 2000. By the way, this module was even older, as if it were built in 1985, as the main module of the Mir-2 station, which was never created. On December 2, 2000, the first crew – William Sheperd, Yuri Gizenko and Sergey Krykalev – rose to board the International Space Station.
In 25 years, 73 basic expeditions and 16 expeditions of visit, with 230 people, plus 94 cargo ships have visited the ISS. The International Space Station is a truly unique project, the most expensive object ever created by humanity-$ 150 billion in 2010, which gives $ 219 billion in prices in 2025, even without supporting support over the last 15 years. The station has allowed to obtain a lot of useful scientific and technical information, to run new technologies and processes, to study the impact of long stay in space on the human body, which is important for the preparation of future interplanetary missions. So it exactly cost it.
Initially, the ISS was designed for only 15 years of operation, ie until 2015. Since then, the mission duration has been extended, last time until 2030. But the components of the station are aging, it is increasingly difficult to maintain in the appropriate state, we recall at least a constant leakage of air in the Russian module “Zvezda”, which began in 2019. Considering which year began to build this module, it is not surprising, he is already 40!
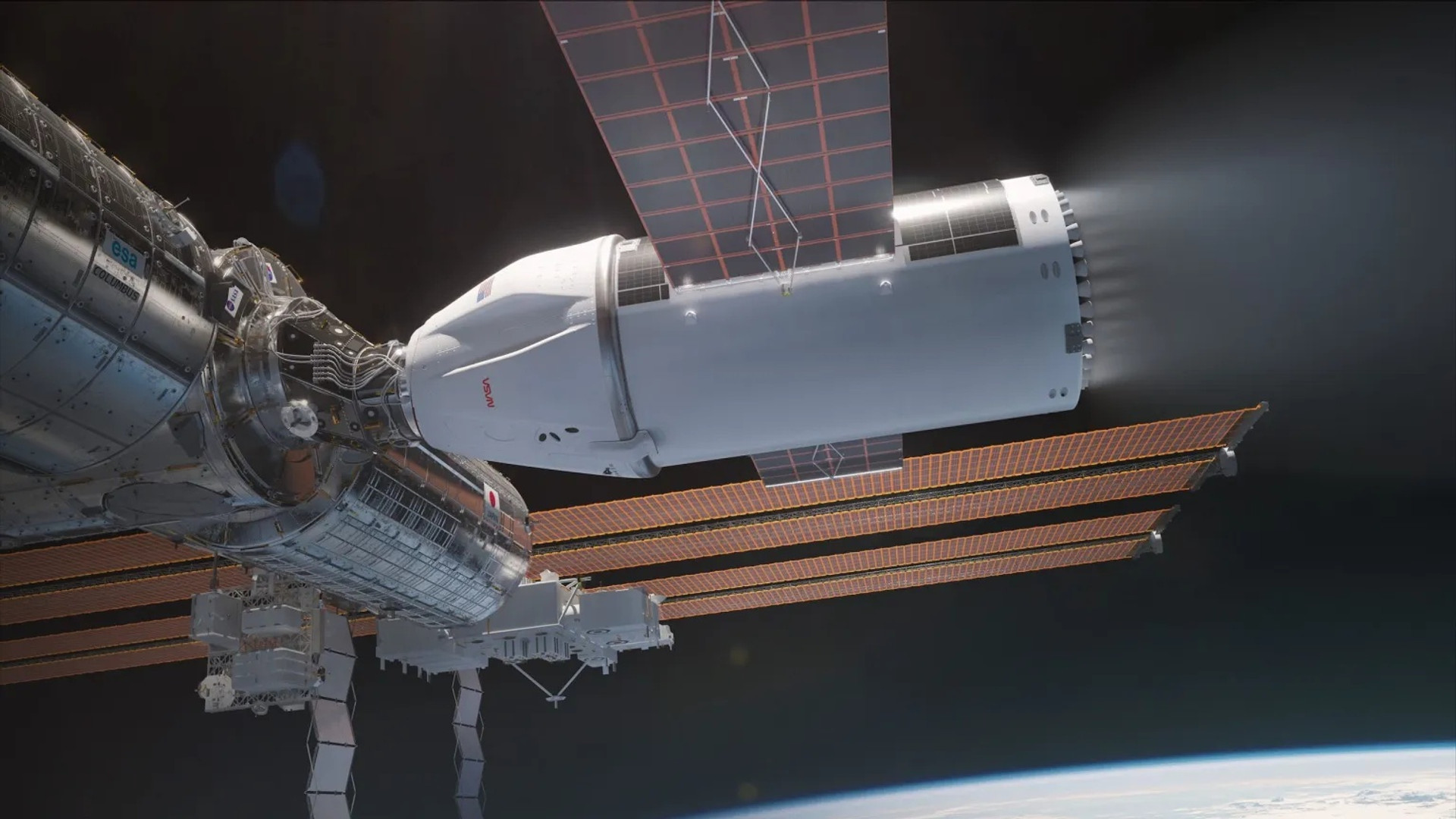 SPACX US Deorbit Vehicle, Render SpaceX Design
SPACX US Deorbit Vehicle, Render SpaceX Design
SpaceX
Therefore, the issue of termination of operation of the ISS has long been theoretical. NASA proposes to build a special ship to erect a station from orbit. In June 2024, it became known that SpaceX would be built, which received a $ 843 million contract for the development and construction of the relevant ship – US Deorbit Vehicle. It will be updated Cargo Dragon plus a large service module of 33 tonnes of fuel and 30 additional DRACO engines – a kind of heavy space tugboat that has to push the station controlled to the bottom of the gravitational well. NASA is scheduled to erect the ISS from orbit for January 2031, although Ilon Musk urges it to do so as soon as possible, over the next two years.
In any case, the time of the International Space Station expires, and there is a natural question what next? Will it be a new international project, or a number of private space stations, as planned according to NASA Commercial Leo Destinations Program? Let’s see what space agencies of different countries are planning in this field, and what private companies offer. But first, as usual, a little story.
Space stations. Theory It is believed that for the first time the concept of the space station was voiced in the story of the American writer and priest Edward Everett Hale “Brick Moon” / The Brick Moon (1869). Of course, it was a very primitive description, but it was a description of an artificial object that rotates around the Earth and should use navigation. Yes, it was a kind of GPS prototype, and the author even guessed that at least four satellites above the horizon were required to navigate.
More scientific and substantiated works on this topic in the 1920s were published by the Austro-German physicist and engineer Herman Rer and Ukrainian scientist Konstantin Tsiolkovsky. The ancestors of the scientist are in fact from Volhynia, they are distant relatives of Hetman Severin Nalyvaika, as Tsiolkovsky himself was very proud of. As for Herman’s rotation, he was a member of the German Society for Max Space Travels, which we have already written about, and his student and assistant at one time was… Werner von Brown, who was very impressed with the test of rocket launchers and rocket vehicles Opel/Valie. Herman Turkey worked with Brown first above FUU-2 in Peremund, and then over the first intercontinental ballistic missile SM-65 atlas in the United States.
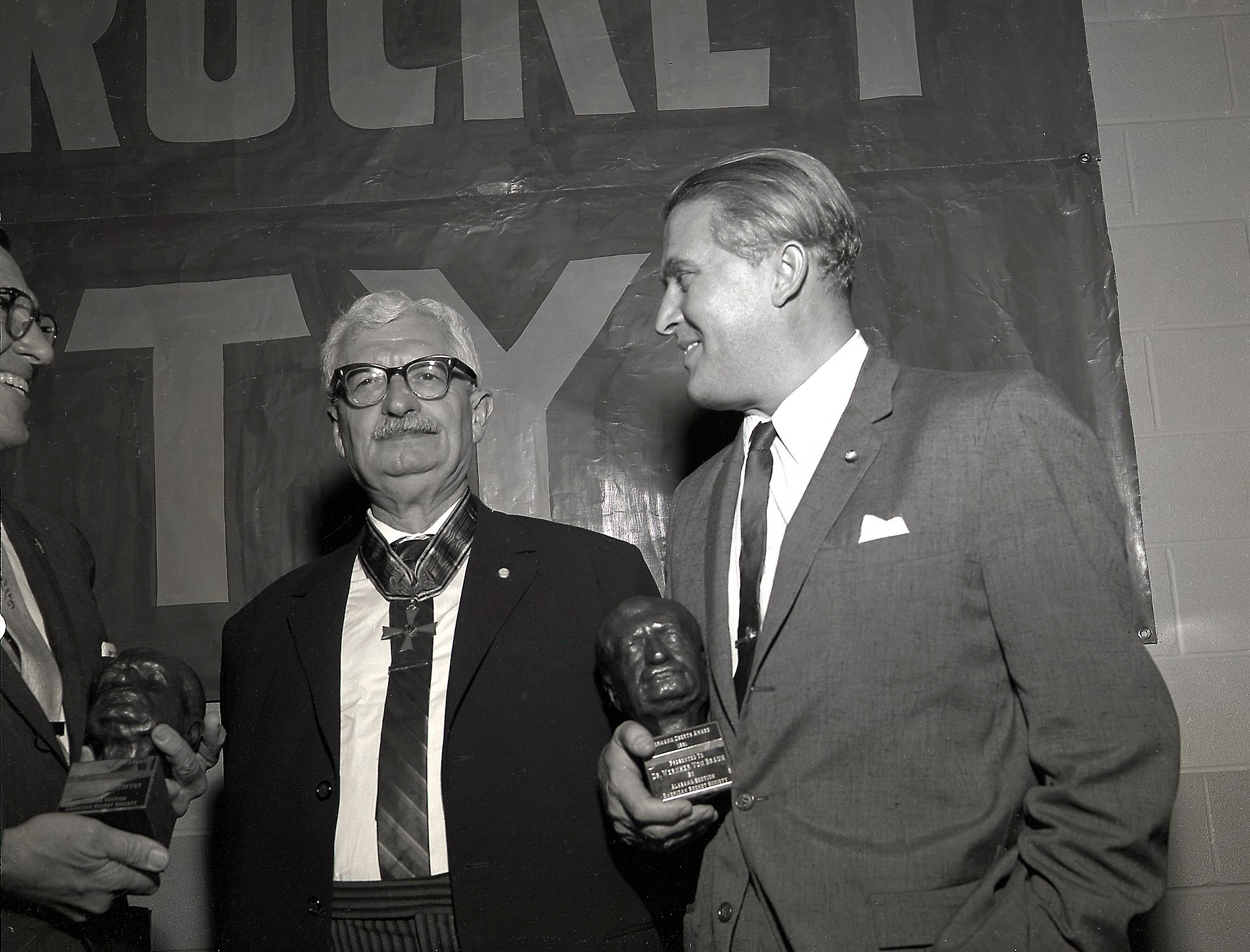 Herman Rer and Werner von Brown, 1961
Herman Rer and Werner von Brown, 1961
NASA
Back in 1929, a space station project appeared to create artificial gravity. These can be seen in numerous fantastic works and films, but in reality they do not exist yet. The drawings appeared in the book of Herman Potocznik (Nickname Herman Nordung) Das Problem Der Befahrung Des Weltraums. Der Raketen-Motor / “Problem Overcoming Space Space. Missile Engine”, which came out in the year of the author’s death.
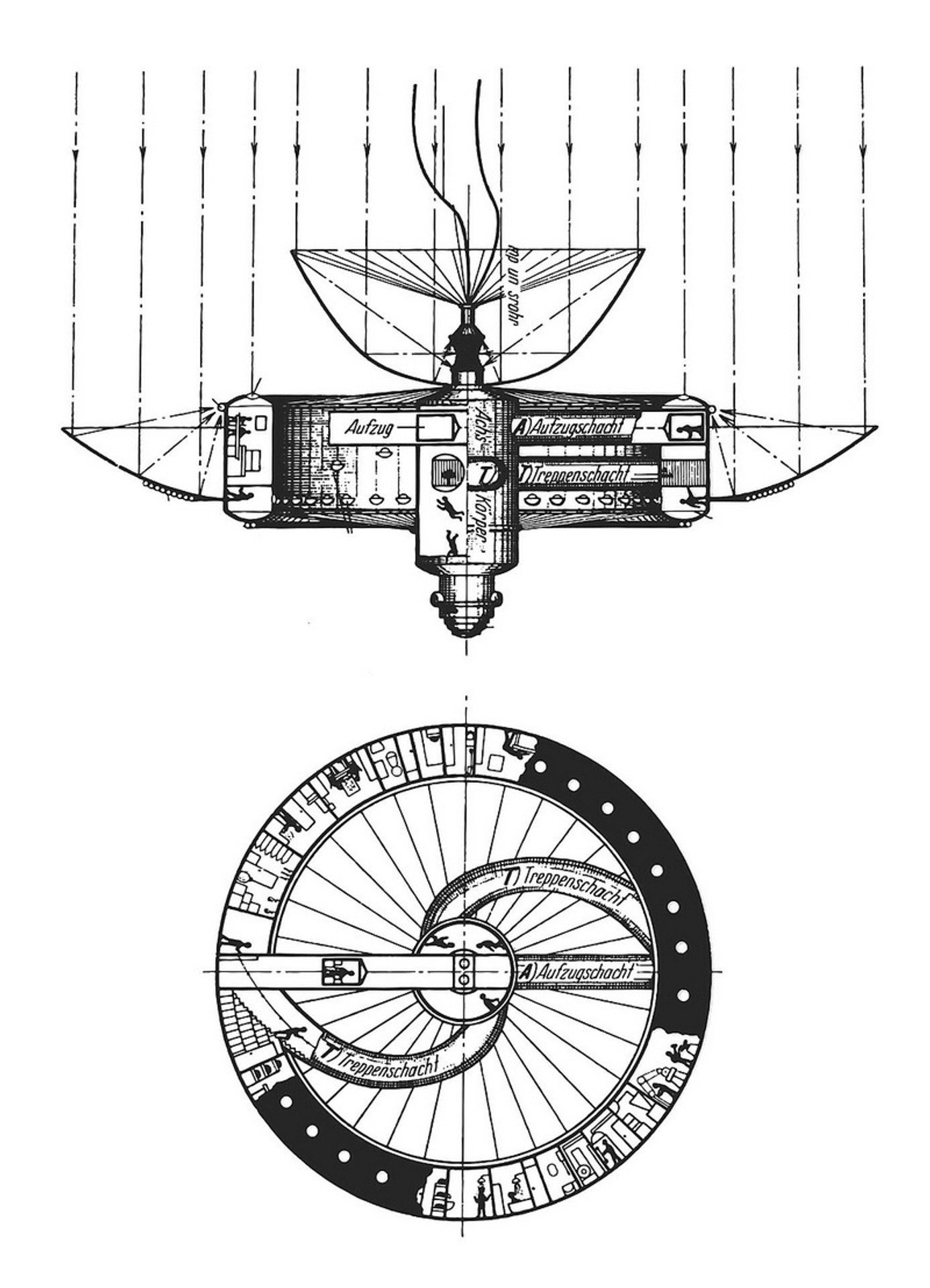 Herman’s Space Station from Das Problem Der Befahrung Des Weltraums. Der Raketen-motor
Herman’s Space Station from Das Problem Der Befahrung Des Weltraums. Der Raketen-motor
Herman Potočnik
And in 1936, Alexander Belyaev’s fantastic novel “The Star Ketz” was published, the events of which occur at the space station, which was named after Konstantin Edward Tsiolkovsky. Prior to the appearance of the first real space station, it remained another 35 years.
Space stations. Practice: “Salute”, “Diamond”, “Mir”, Skylab, Tiangong The world’s first space station, “Salute-1”it was launched in orbit by the proton-K rocket on April 19, 1971. According to Soviet mythology, the USSR was not interested in the development of the month, so it seemed to be concentrated on the construction of space stations and long -term flights. In fact, the USSR lost the race to the moon and had a chance to lose the racing to create a Earth’s station, because the US project SkyLab was already in development, so it was decided to create and launch at least something.
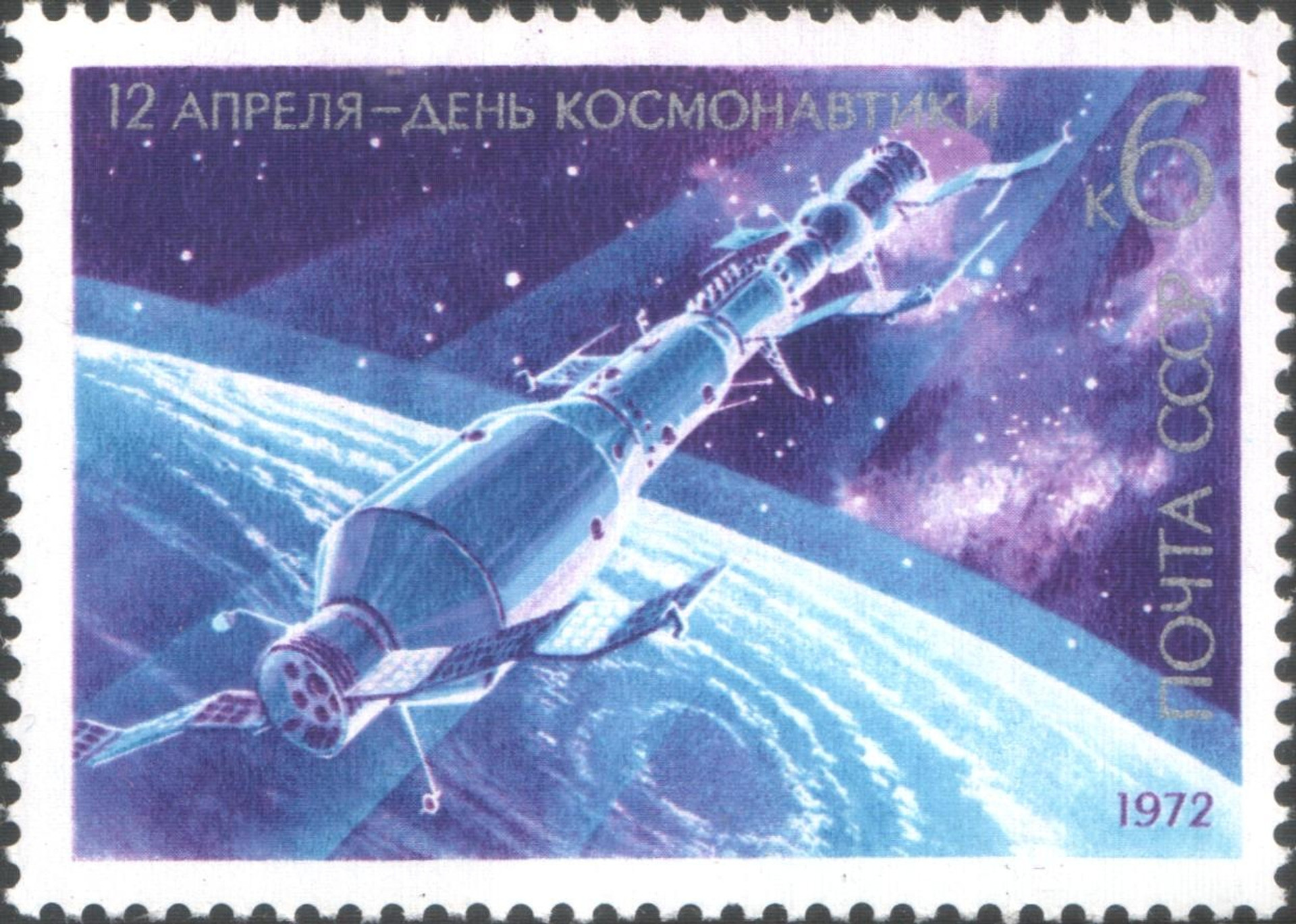 Salute-1 station on the USSR brand
Salute-1 station on the USSR brand
USSR mail
Salute-1 and became something. In fact, it is a kind of civil modification of the Military Station of the Diamond project, which the intelligence cosmonauts had to observe NATO objects. Diamond development was delayed, so it was decided to launch Salute.
In fact, it was only after the collapse of the USSR to the general public that from the seven space stations of the Salute program, only four were conditionally civil, three other-Salute-2, Salut-3 and Salut-5 were military. Moreover, they even had defense weapons in case of “interest” on the side of American satellites-modified for use in space 23 mm Turel aircraft gun P-23 AA Riter system, known as P-23M “Cartard”. From the gun to “Diamond” 101.2 / “Salute-3” even made test shootings (the guidance was rotated by the entire station), which makes “Salute-3” the only known, as of now, the combat spacecraft. “Diamond” 104, which was never built, seemed to be armed with the space-cosmos system.
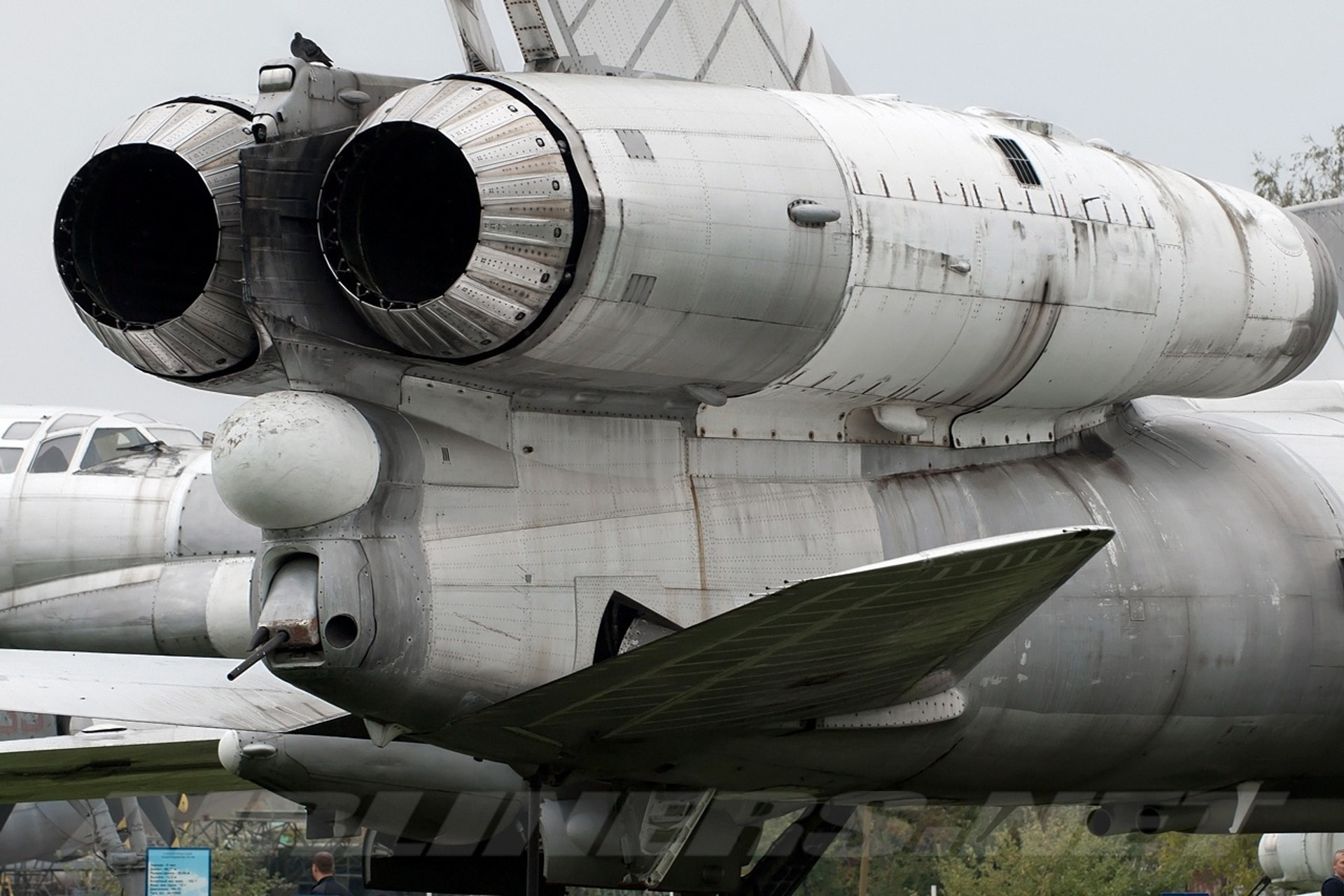 Aviation Garma R-23 on TU-22PD Detainer
Aviation Garma R-23 on TU-22PD Detainer
Alex Beltyukov
But back to Salute-1. The station spent 175 days in space and adopted two crews of three people who spent only 24 days on board.
The next launch under the Salute program on July 29, 1972 was unsuccessful. Due to the failure in the second degree of the proton-K rocket launcher, the station did not go into orbit and fell into the Pacific. According to the Soviet habit, the failure was hidden and this station did not even get its own name, so known as DOS-2 (Long -term orbital station).
The United States lost to the creation of space stations. The first American station, Skylabwas launched only on May 14, 1973. Skylab, which was built from the extra third degree of S-IVB of the Saturn V Monthly Rocket, was simply a giant compared to Salute-1. 360 m³ inner space vs. 90-100 m³ In the stations of the Salute series, two “floors”, a shower, separate, though small, crew cabins.
Skylab received some damage during the launch – the micrometeoric shield was incorrectly opened, which, among other things, had a sunlight from the sun’s rays, and did not open one of the solar panels. Therefore, the first crew, which started on May 25, 1973, was to repair the station.
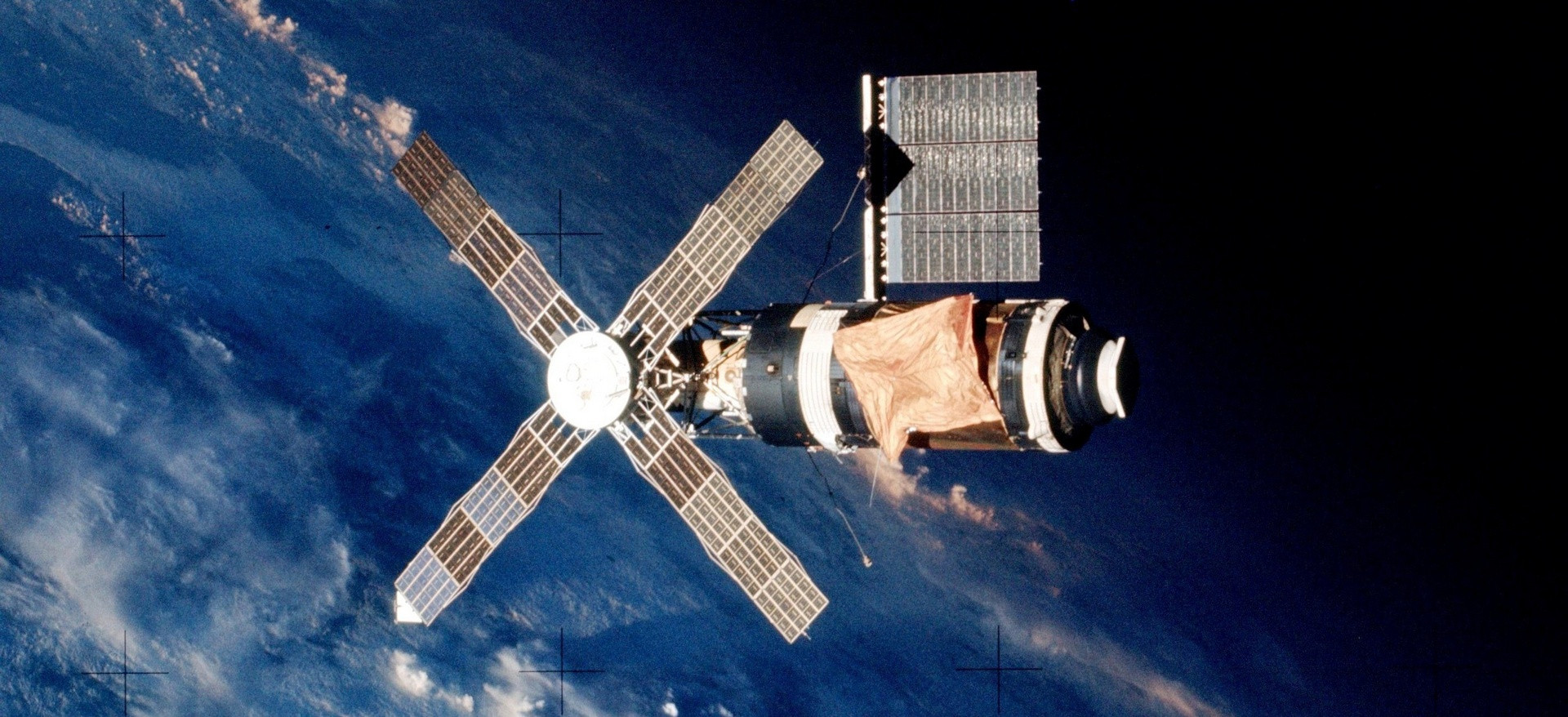 Skylab station from the Apollo CSM-116 ship of the first expedition. The crumpled micrometeoric shield and not open solar panel are visible
Skylab station from the Apollo CSM-116 ship of the first expedition. The crumpled micrometeoric shield and not open solar panel are visible
NASA
In total, Skylab spent 2249 days in orbit and adopted three crews of three people who spent 171 days at the station. On board, a bunch of interesting experiments was carried out, for example, the study of X -ray radiation of the sun led to the emergence of X -ray astronomy. Riccardo Jakconi received the 2002 Nobel Prize for this.
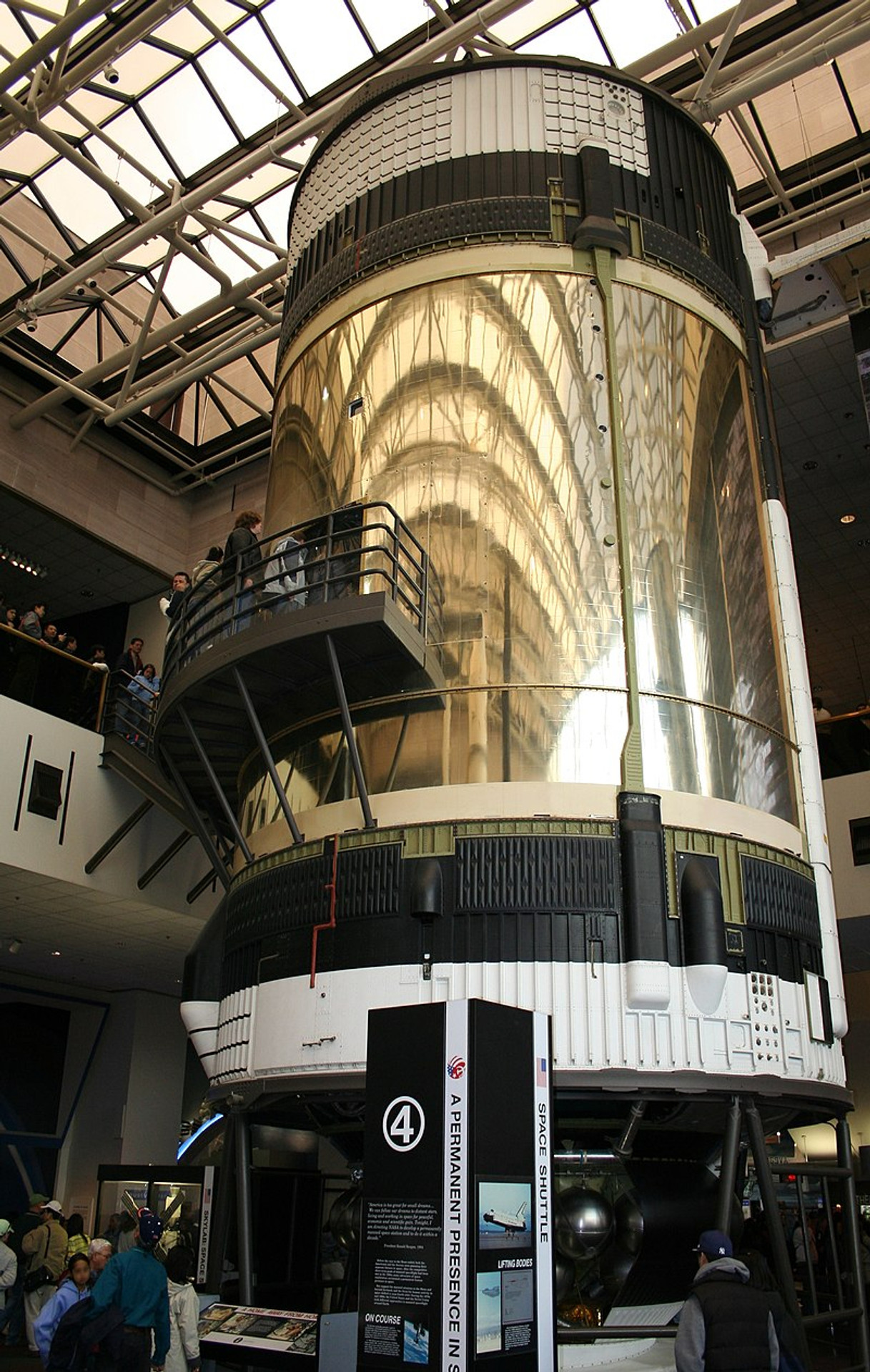 Skylab B (S-IVB 515) station at the National Aviation and Space Museum, Washington, District
Skylab B (S-IVB 515) station at the National Aviation and Space Museum, Washington, District
SKPY
Unfortunately, NASA abandoned Skylab in favor of Space Shuttle and the Freedom modular station, which the agency planned to build in the 1980s and 1990s. The fourth expedition of the visit, SkyLab 5, which was to take place in April 1974, was canceled. The second station, Skylab B, which they even managed to build, never launched. Apollo – Union in 1975 became the last man -made mission of Apollo – Union, and then the Americans stopped launching people into space for 6 years, before the first start of Columbia Shatle on April 12, 1981.
The abandoned Skylab burned in the Earth’s atmosphere on July 11, 1979. The descent was partially controlled, so some fragments fell in Australia.
 So would have to look fully collected American Freedom Station
So would have to look fully collected American Freedom Station
NASA
Let us return to the Soviet Union. The next launch of Salute program, which took place on April 3, 1973 in orbit “Salute-2”which we recall was actually a military “Diamond” 101.1. On the 13th day there was a depressurization of the compartments, on April 25, telemetry stopped coming and on May 28, 1973, the station left orbit and fell in the Pacific near Australia. There was no visit expeditions.
Salute-3, which started three days before Skylab, May 11, 1973, was also not lucky. After entering the orbit due to failure of the orientation system, uncontrolled switching on the engines and rotation of the station began, and after all the fuel was spent, the station was doomed. According to the Soviet habit, unsuccessful launch was marked “Space-557”. On May 22, 1973, the station left orbit.
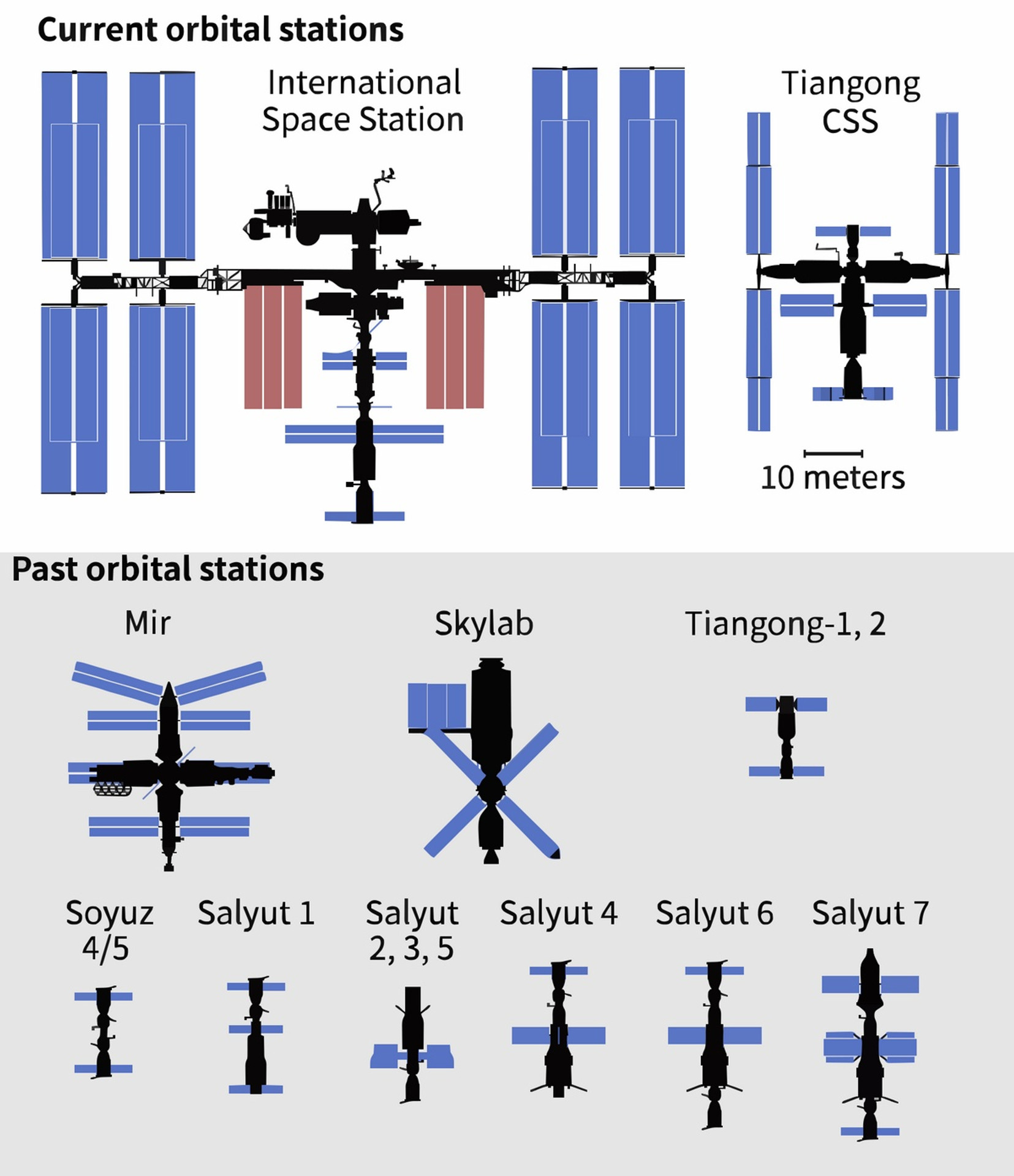 Comparative size of space stations of different generations, graphics
Comparative size of space stations of different generations, graphics
Thomas Shafee
The next station that has finally received an official name “Salute-3”although it was actually a military Diamond 101.2was launched on June 25, 1974 and spent 213 days in orbit. During this time, only one visit took place – two military astronauts were held at the station for 15 days, after completing the mission, they tested the same space gun mentioned above.
The next station, conditionally civil “Salyut-4”She spent more than two years in orbit, from December 26, 1974 to February 3, 1976, two expeditions for two astronauts each. Another expedition, which was planned for April 1975, broke out due to the accident of the Soyuz rocket, the crew of the Soyuz-18A ship survived. In addition, the station visited an automatic Soyuz-20, a kind of prototype of future cargo ships “Progress”.
Station ”Salute-5 “ Aka Diamond 103was also military. She spent 412 days in orbit (June 22, 1976 – August 8, 1977). There were three expeditions of the visit, but one of them, on the Union-23, could not do the dock, so only four astronauts visited the station. It was the last military intelligence station of the USSR, as it turned out, automatic intelligence satellites are easier and cheaper to use.
Really successful became the station “Salute-6” (September 29, 1977 – July 22, 1982). There were also the main long -term expeditions, expeditions of visit, and the use of cargo ships “Progress” and TKS (“Snabzhienia transport ship” – a cargo / optional manned ship that was supposed to work with the stations of the Diamond series). The station spent 1764 days in orbit, 683 of which it was inhabited. A total of “Salute-6” visited 16 crews of 33 astronauts and 14 cargo ships. The longest expedition is 185 days, Leonid Popov and Valery Ryumin. It was at Salut-6 that the Soviet Union began to collect unique information on the long stay of man in space.
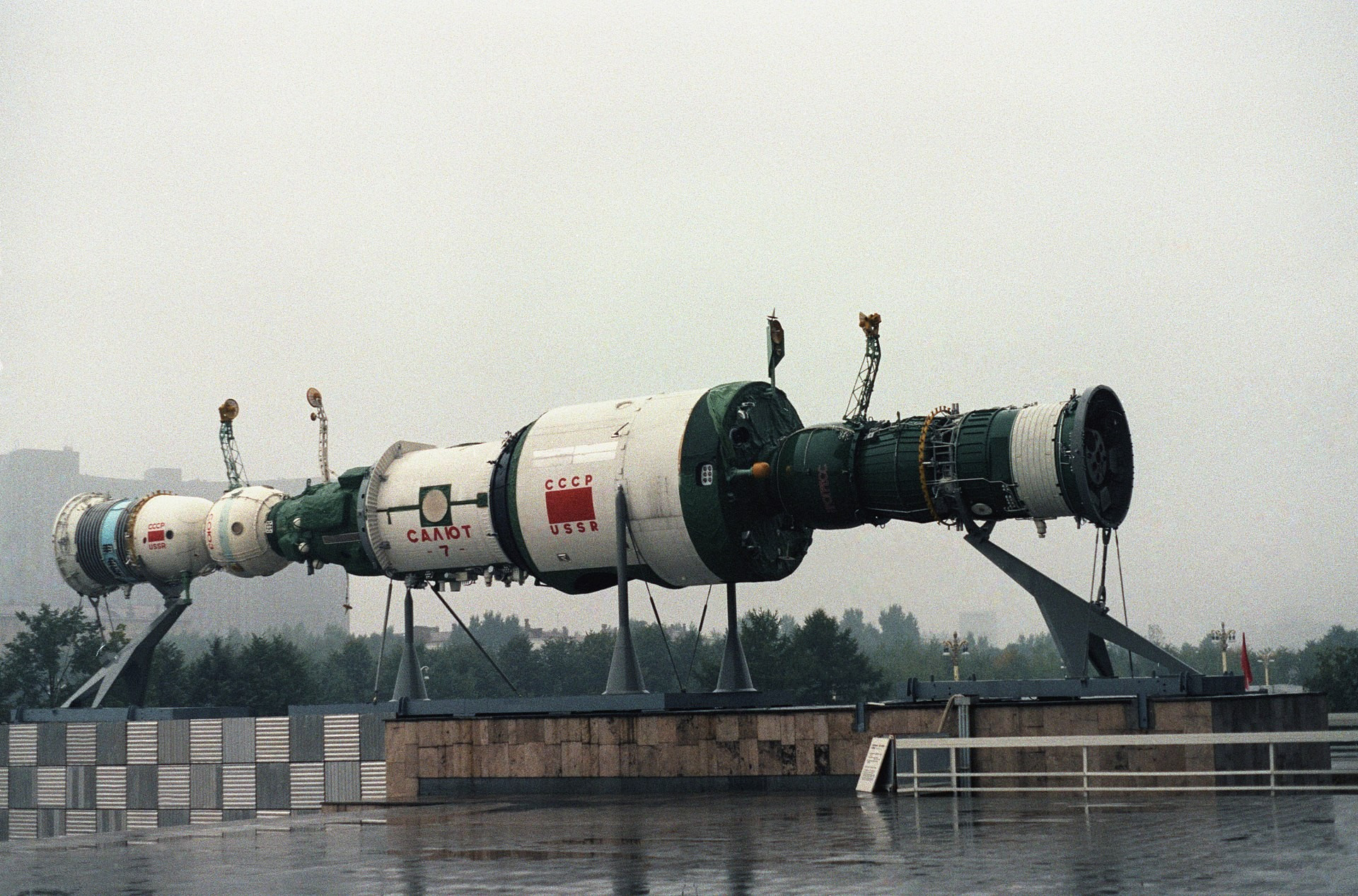 Salyut-7 layout with Soyuz and Progress ships on VDNG, Moscow
Salyut-7 layout with Soyuz and Progress ships on VDNG, Moscow
DON S. MONTGOMERY
The last station of the monoblock structure has become “Salute-7”which was in orbit from April 19, 1982 to February 7, 1991, most of the time in non -piloted mode, because since 1986 the USSR began the operation of the next station – the modular “Peace”. Salut-7 accepted 10 expeditions and 15 cargo ships, and 22 astronauts visited it, which, among other things, set a regular record of duration of stay in space. Kizim / Solovyov / Otkov crew spent 237 days in orbit.
Unlike Salute Stations https://mezha.media/ “Diamond” and American Skylab, which were one -volume (conditionally warship ship supply to TCS can be counted as a separate module, but very conditional), “Peace” It consisted of the last stage of existence of 7 modules. This is what the American Freedom had to be, but this project was postponed and delayed, although the Space Shuttle program was created not the last way for the construction of the orbital station.
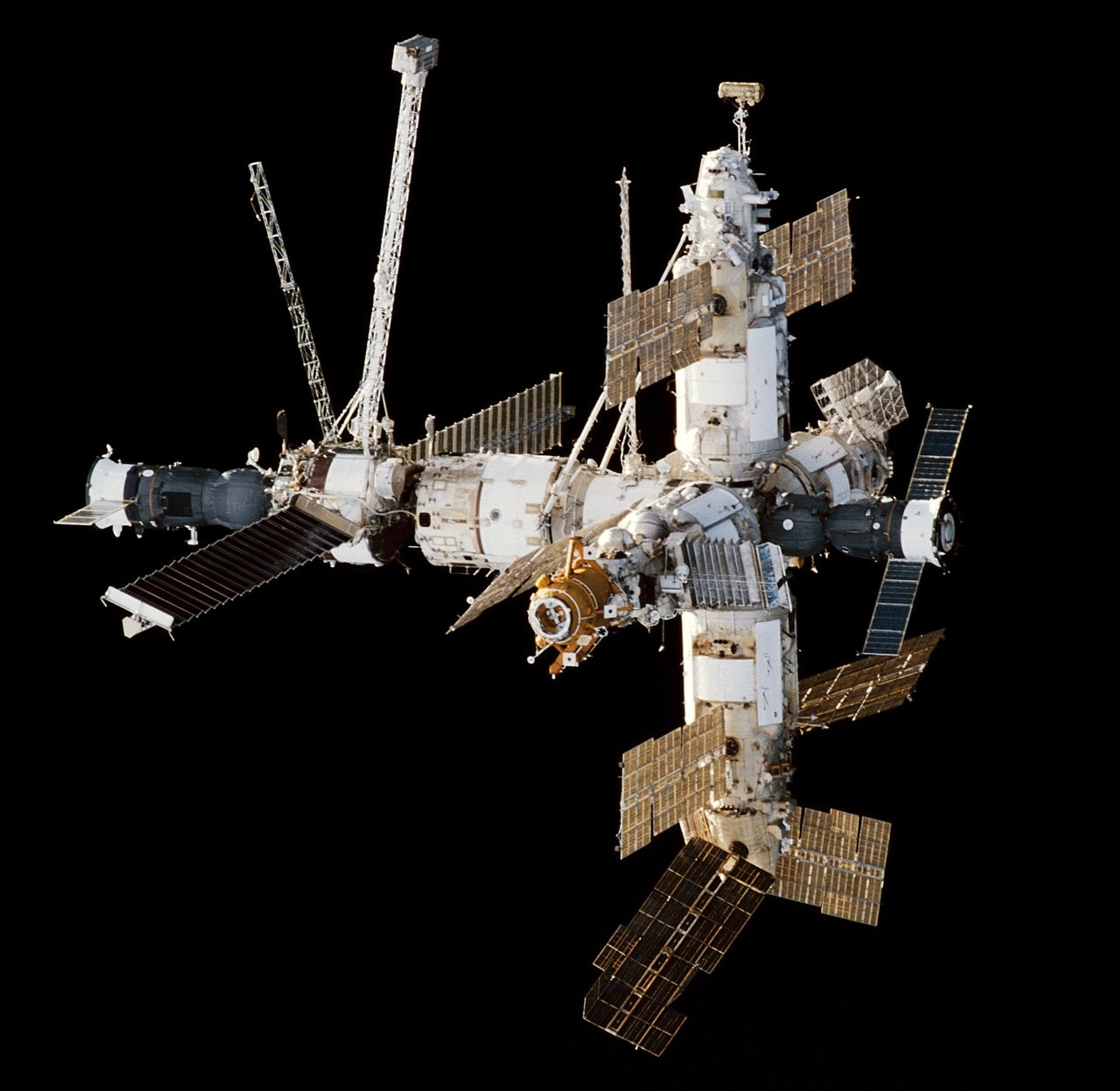 View at Mir Station from Endeavur Tent, 1998
View at Mir Station from Endeavur Tent, 1998
NASA
The construction of Peace began on February 20, 1986, when the proton-K rocket launcher launched into the orbit of the base module of the station, which was created at the works of the base module “Salute”. We will remind, “Zvezda”, the main module of the International Space Station is the Dos-8 AKA “Mir-2”, so yes, the ISS is based on the technologies of “Salute”, that is, the technology of 50 years ago.
On April 12, 1987, the Astrophysical Module “Quant” was reconciled to the Mir. December 6, 1989-Scientific and Ground Module “Quant-2”. On July 10, 1990, the Crystal joint and technological module. June 3, 1995 – Spectrum Research Module. On November 15, 1995, a connective module for the shutters was added to the station, which delivered an Atlantis shuttle.
The Americans have joined the Mir exploitation, first and foremost, to gain experience for the construction of the ISS and attract the Russians and their works. In matters of long flights and construction of space stations of the USSR and Russia, which followed the space achievements of the Soviet Union, the United States really significantly ahead of the United States.
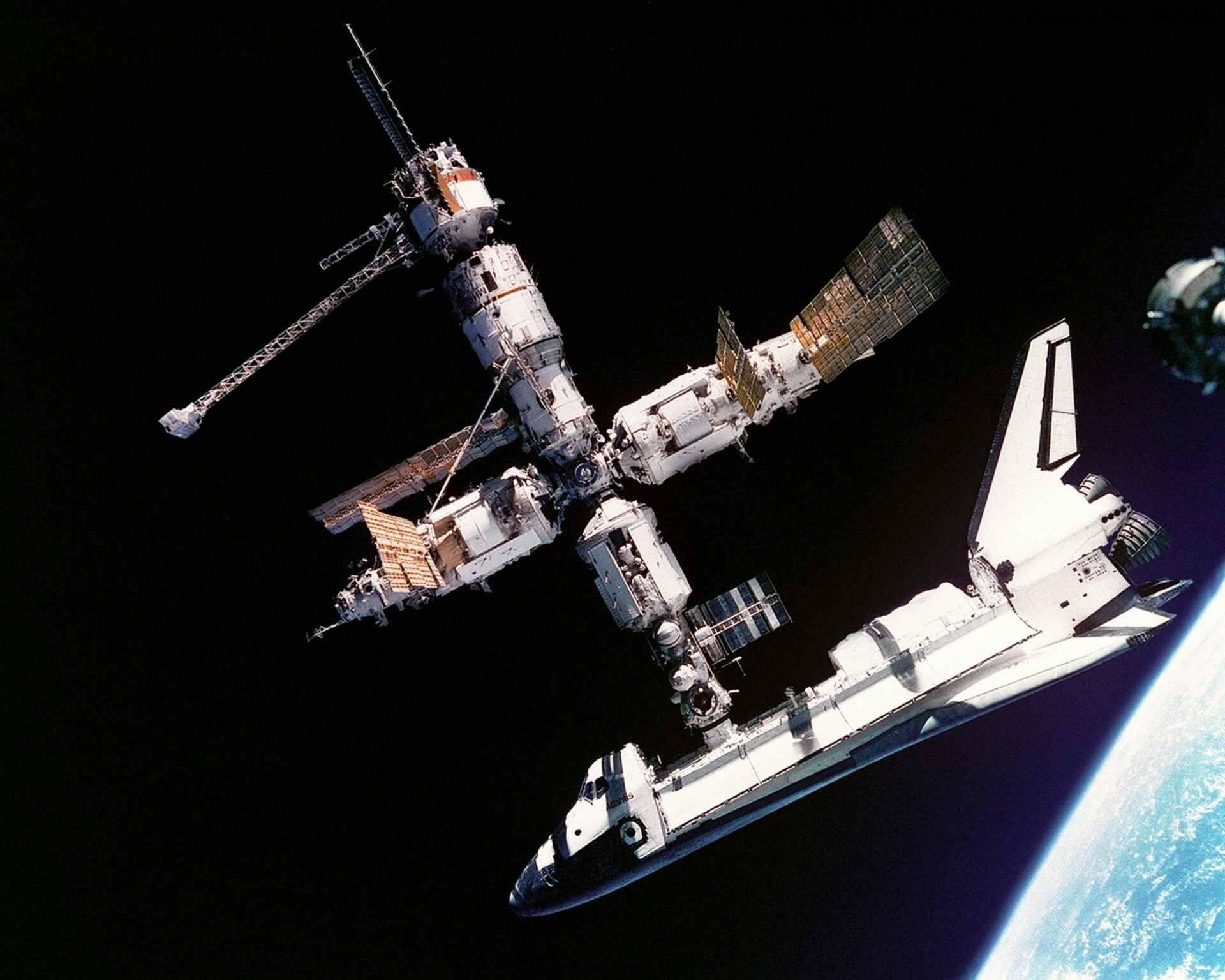 Atlantis Shatl is stamped with Mir Station, July 3, 1995.
Atlantis Shatl is stamped with Mir Station, July 3, 1995.
NASA
MOCS cooperation and program Shuttle – Mir It began in 1993. On February 3, 1994, the first Russian flew in the tent, March 14, 1995 – the first American at the Union. Unfortunately, this cooperation is still ongoing. The first joint of the Atlantis shuttle to the Mir station took place on June 27, 1995, a little later the same Atlantis brought to the station more convenient for the shutters. A total of 12 missions were made under the Shuttle – MIR program, including long -term flights from several US astronauts.
The last, seventh module of “Peace”-the research “Nature” was adhered to the station on April 26, 1996. Kharkiv Hartron joined the development of almost all Mir modules, and his specialists were responsible for the control system.
Most of the time of “Mir”, which was in orbit from February 19, 1986 to March 23, 2001, was inhabited. The station visited 125 people in the course of 39 managed missions and 68 cargo ships. Interestingly, despite the large number of modules, “Peace” was inferior to the old Skylab by sealed volume – 350 m³ against 360 m³.
The station conducted a record number of scientific experiments – 23 thousand cosmonaut Valery Polyakov in 1995 established and still a not -to -take the record of continuous stay in space – 438 days. In 1997, the station survived a fire and a collision with the M-34 Progress.
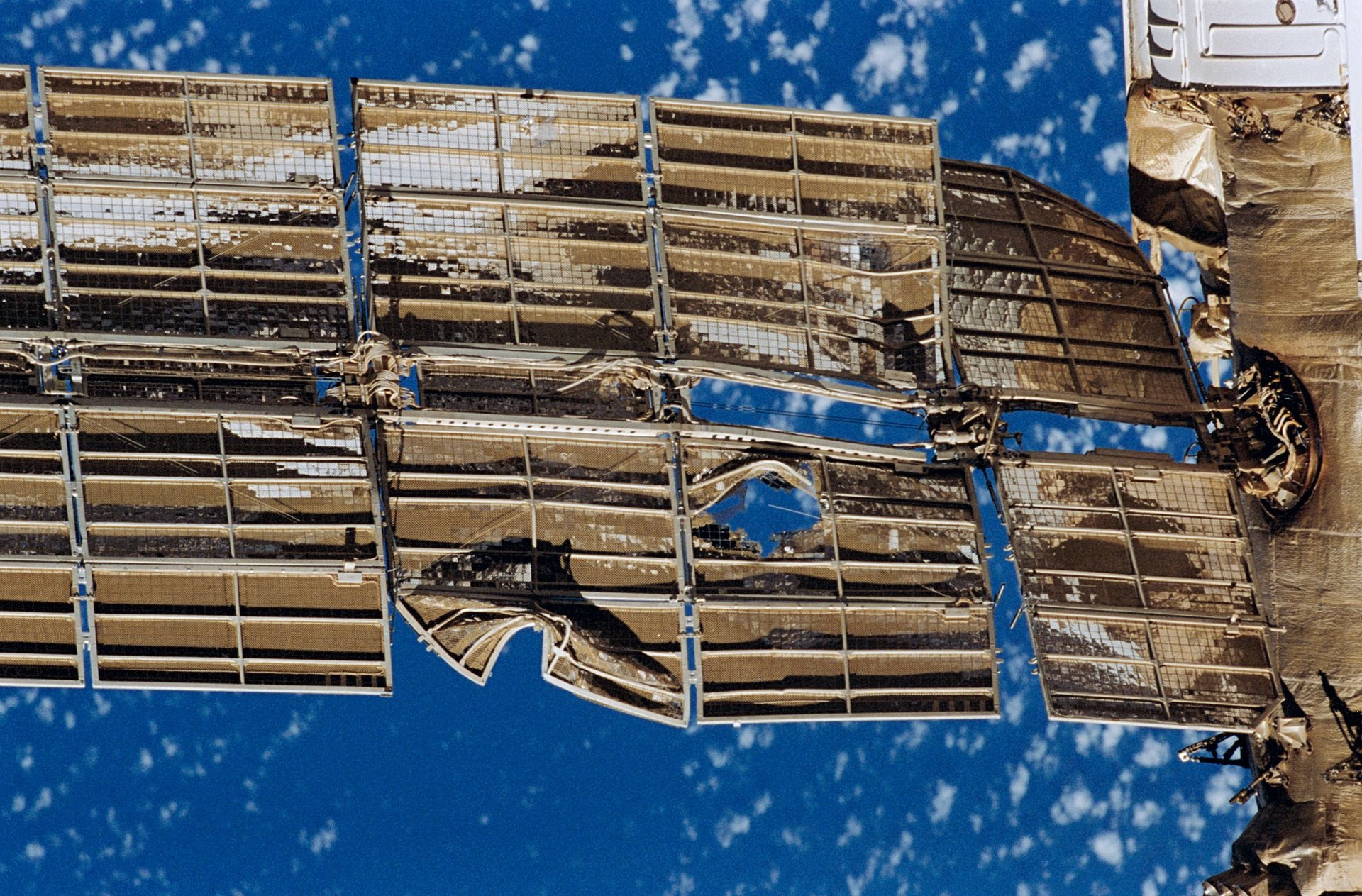 The consequences of the collision of the Mir station with the cargo ship “Progress M-34” June 25, 1997. In the photo, the solar panels of the Spectrum module module
The consequences of the collision of the Mir station with the cargo ship “Progress M-34” June 25, 1997. In the photo, the solar panels of the Spectrum module module
NASA
“Mir” was continuously inhabited for almost 10 consecutive years – from September 5, 1989 to August 28, 1999. Already in 1998, the old station began to be cooked, but the erection process was detained from the orbit, because private investors seemed to have extended the life of the Peace.
The Mircorp Corporation found money and financed another manned-“TM-30 Union” (April 4, 2000-July 16, 2000) and another cargo flight to the station. The station was reactive and tried to repair and turn into an orbital film studio. What movies were about to shoot in space we will not show you. And no, this is not hardcore porn, but much worse is Russian cinema.
Fortunately, “Mir” was no longer operable, but Mircorp was over. On March 23, 2001, the station was erected from orbit and flooded in the Pacific. At this point, the ISS already had four modules and the second expedition worked at the new station.
But before we go to modern stations, it is worth mentioning two Chinese Tiangong-1 test stations and Tiangong-2, which were in space from September 29, 2011 to April 2, 2018 and from September 15, 2016 to June 19, 2019, respectively.
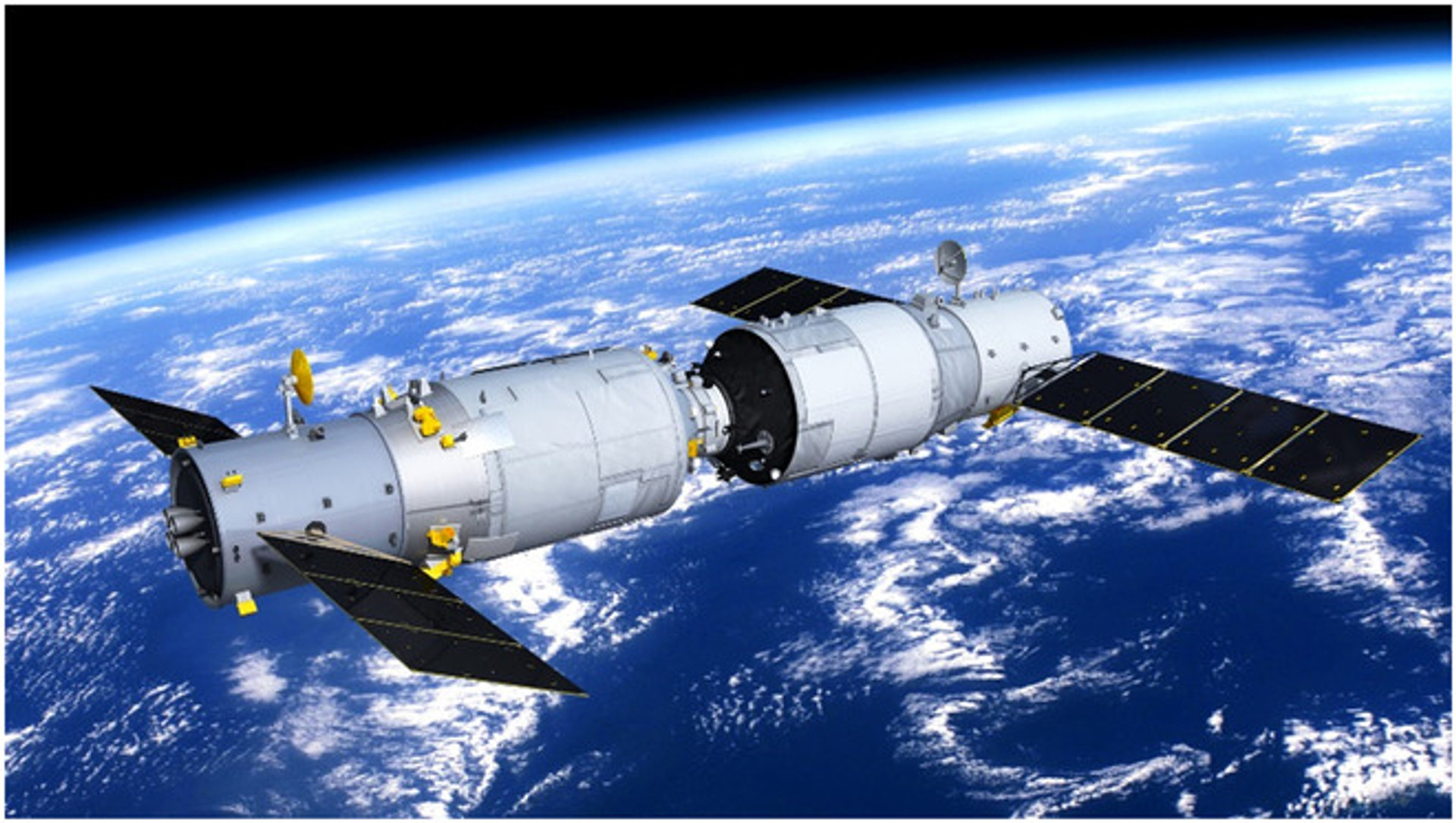 Tianzhou-1 automatic cargo ship and Tiangong-2 (right) station, render
Tianzhou-1 automatic cargo ship and Tiangong-2 (right) station, render
Jianyu lei
Tiangong-1 and Tiangong-2 were the prototypes of the main module of the future Tiangong space station, as well as test platforms for the work of ripening and joining procedures. Both stations had a scanty tight volume – only 15 m³ against 90–100 m³ Salut stations of various modifications. Test stations can be compared to the size, mass and volume with Chinese man -made ships of the Shenzhou series, which, in turn, are variations on the theme of the Soviet Union.
However, Tiangong-1 and Tiangong-2 visited three expeditions of 8 Taikovt, which spent 51 days on them. In addition, there were two joints of cargo ships. The necessary information was collected, and the PRC began to develop a full -fledged modular space station.
Space stations. Modernity: MKS, Genesis, Tiangong As of now, two large modular stations operate in orbit – an international space station (mass 450 tons, volume – 1 005 m³) and Chinese tiangong (weight 100 tonnes, volume – 340 m³).
Plus two more experimental inflatable modules Genesis i (Running July 12, 2006) and Genesis II (Running June 28, 2007) from Biglow Aerospace based on the NASA Transhab concept of the 1990s. The module equipment has transmitted data for 2.5 years, although the missions were only designed for half a year. Unfortunately, since 2020, Biglow Aerospace has actually stopped their activities, although their inflatable Biglow Expandable Activity Module (Beam) module still remains at the ISS. Beam has been attracted to the Transquility module in 2016, so this “Communication” is soon 10 years old.
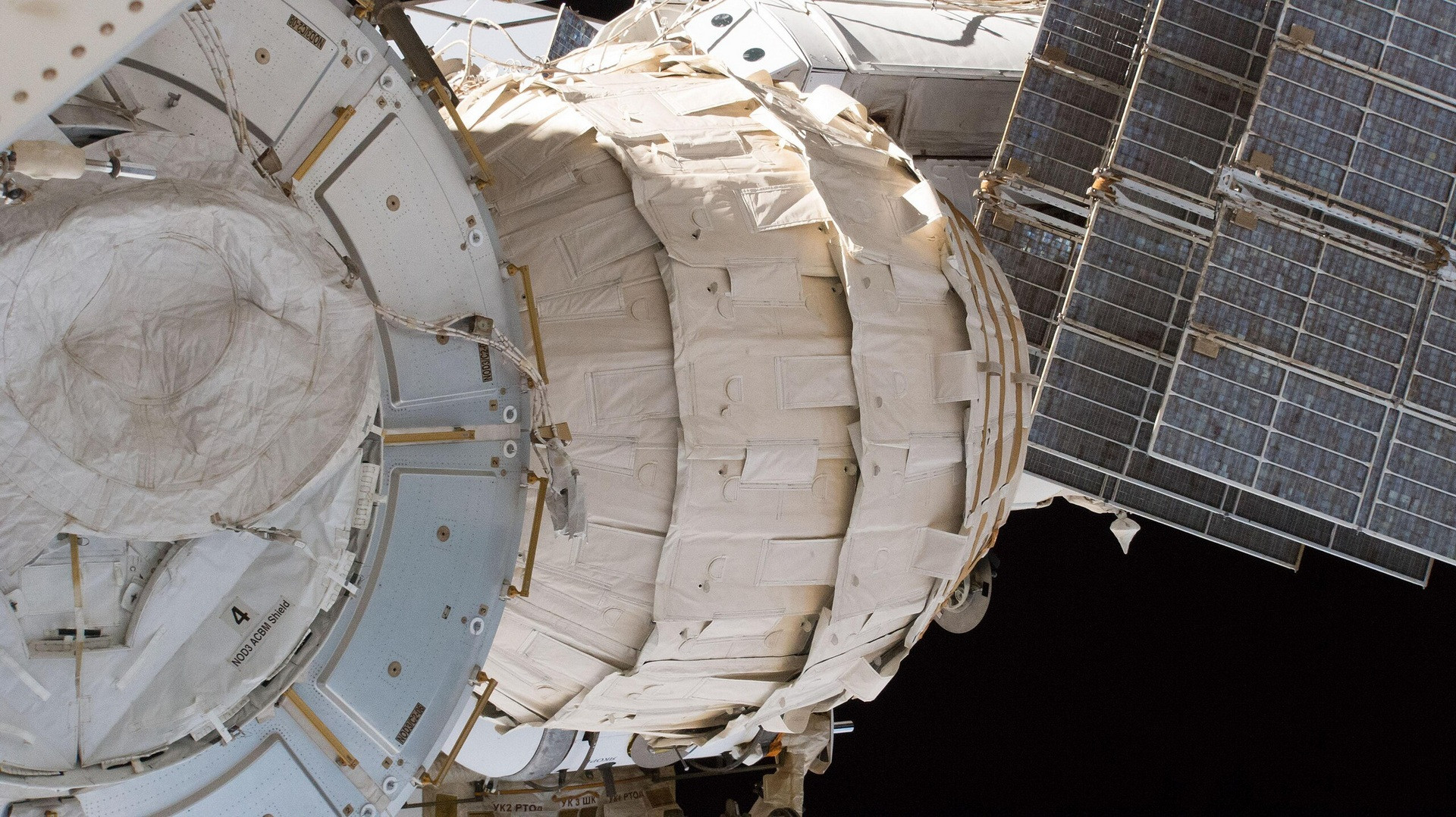 BigLow Expandable Activity Module (Beam) is holding on MCS, 2017
BigLow Expandable Activity Module (Beam) is holding on MCS, 2017
NASA
About the value and current state International Space Station We wrote at the beginning of the article, in addition, the ISS is constantly in the news, so it is pointless to write about it. But the information about the Chinese Tiangong station is much smaller, there are almost no quality photos.
Tiangong ( # 3 of this station was decided not to be assigned) based on the same experiments with Tiangong-1 and Tiangong-2 and the experience of building the Station “Mir”. Even in size, mass and internal volume Tiangong is close to “Peace” – 129 700 kg and 350 m³ In “Mira”, 100,000 kg and 340 m³ In tiangong.
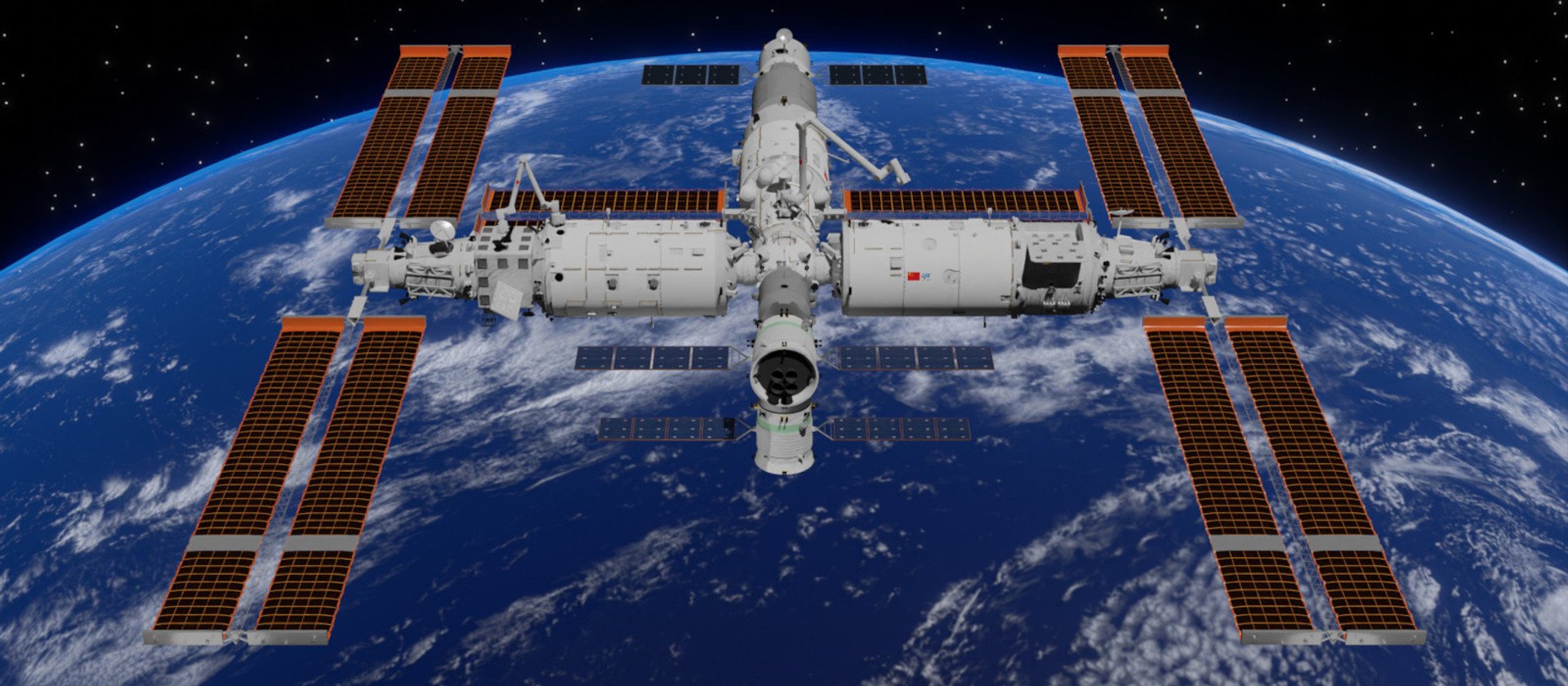 Tiangong station as of March 2023 year, render
Tiangong station as of March 2023 year, render
Shujianyang
The construction of Tiangong began with the launch of the base module Tianhe on April 29, 2021. By and large, Tianhe repeats the configuration and functionality of the basic module of the Station “Mir” So … Yes, the same “Salute” / “Diamond”. Already on May 29, 2021, the Tianzhou cargo ship was rolled up to the station, and on June 17, 2021, the first expedition on the Stenzhou ship 12 arrived, whose design was based on Soviet Unions. Since then, visiting the station has become regular.
In 2022, Tiangong received two additional modules-Wentian laboratory modules (July 24, 2022) and Mengtian (October 31, 2022), both based on Tiangong-2. Tiangong has two robotic arms, and the stations of the station are very reminiscent of the APAS-89/Apas-95 connecting units used for the ISS.
Tiangong has already visited 9 expeditions and 8 cargo ships, 27 tailov spent 1436 days at the station. Tiangong is confidently holding the first place in terms of population / uninhabited. China plans to invite in the future to the station and astronauts of other countries, of course, by analogy with the Soviet “intercosmos” only those who need China. A kind of cosmic diplomacy. The first foreigner on board Tiangong should be a Pakistani.
 Chinese Taicons Van Yapin conducts classes for schoolchildren, October 2021
Chinese Taicons Van Yapin conducts classes for schoolchildren, October 2021
CMSA
China Manned Space Agency (CMSA) plans to expand Tiangong to 6 modules. The new modules should be improved versions of Tianhe, Wentian and Mengtian and reflect them, that is, the station will remain symmetrical. The total mass of Tiangong in this case will be about 180 tons. The new section should have an observatory, another robotic hand, 3D printers and more. The planned life of the station is 15 years, that is, at least by 2036.
And the next “Tiangong” module should be the Xuntian Space Telescope, a kind of Chinese Hubble, but better and built on modern technologies. In this case, Xuntian will not be stuck to the station, but will be in the same orbit, but with different phases, which will allow you to visit the telescope from time to time, or even join it to the station for maintenance and refueling. Xuntian should go into space in 2026.
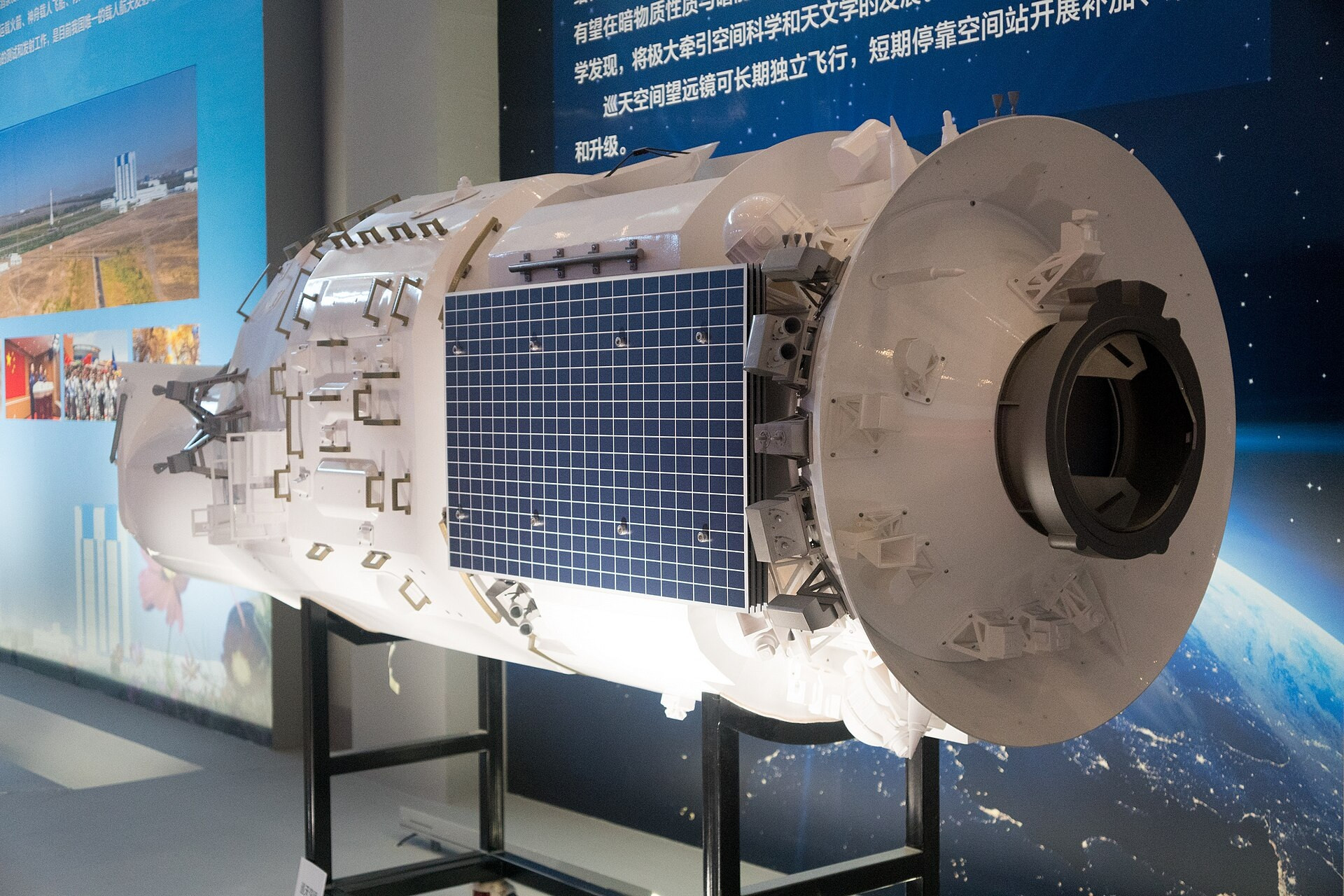 Model of Space Telescope Xuntian, view from the side of the joint unit, National Museum of China, 2023
Model of Space Telescope Xuntian, view from the side of the joint unit, National Museum of China, 2023
Shujianyang
As you can see, the PRC has not grazed the rear for a long time and after the ODIs of the ISS, it is Chinese Tiangong that can remain the only space station in the orbit of Earth. So next time we look at what they offer as an alternative to space agencies of different countries and private companies. Including NASA Commercial Leo Destinations Program as part of the initiative.
